OpenStackのdeploy方法についてはdevstackやらfuelやらtripleOがあるけど、ここではRDO/packstackの設定についてメモを残しておく。
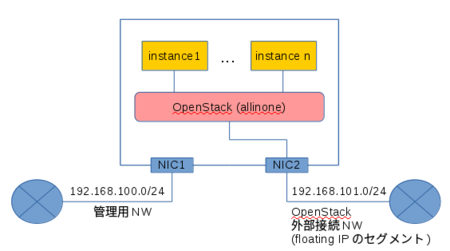
基本的にはRDOのQuickStartに従って構築していくわけですが、今回は下の図のようにNICが2枚刺さっているAllinone構成のOpenStack環境を作る。ちなみにOSはCentOS7。
1. NetworkManagerサービスの無効化
# systemctl stop NetworkManager # systemctl disable NetworkManager
2. NICの設定とnetworkサービスの有効化
# cat /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0 HWADDR=<MAC Address> TYPE="Ethernet" BOOTPROTO="dhcp" NAME="eth0" ONBOOT="yes" IPADDR="192.168.100.2" NETMASK="255.255.255.0" GATEWAY="192.168.100.1"
# cat /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth1 HWADDR=<MAC Address> TYPE="Ethernet" BOOTPROTO="dhcp" NAME="eth1" ONBOOT="yes" IPADDR="192.168.101.2" NETMASK="255.255.255.0" GATEWAY="192.168.101.1"
# systemctl restart network # systemctrl enable network
3. 最新パッケージへのupdate
# yum update -y
4. rdoリポジトリの登録とpackstackのインストール
# yum install -y https://rdo.fedorapeople.org/rdo-release.rpm # yum install -y openstack-packstack
5. packstackの設定ファイルの作成
$ packstack --gen-answer-file=packstack-answer.txt
6. 設定ファイルの修正
適宜環境に合わせてupdateする。今回作成した設定ファイルは次のとおり。
$ cat packstack-answer.txt [general] # Path to a Public key to install on servers. If a usable key has not # been installed on the remote servers the user will be prompted for a # password and this key will be installed so the password will not be # required again CONFIG_SSH_KEY=/home/satoru/.ssh/id_rsa.pub # Set a default password everywhere. The default password will be # overriden by whatever password is set for each individual service or # user. CONFIG_DEFAULT_PASSWORD=<password> # Set to 'y' if you would like Packstack to install MariaDB CONFIG_MARIADB_INSTALL=y # Set to 'y' if you would like Packstack to install OpenStack Image # Service (Glance) CONFIG_GLANCE_INSTALL=y # Set to 'y' if you would like Packstack to install OpenStack Block # Storage (Cinder) CONFIG_CINDER_INSTALL=y # Set to 'y' if you would like Packstack to install OpenStack Compute # (Nova) CONFIG_NOVA_INSTALL=y # Set to 'y' if you would like Packstack to install OpenStack # Networking (Neutron). Otherwise Nova Network will be used. CONFIG_NEUTRON_INSTALL=y # Set to 'y' if you would like Packstack to install OpenStack # Dashboard (Horizon) CONFIG_HORIZON_INSTALL=y # Set to 'y' if you would like Packstack to install OpenStack Object # Storage (Swift) CONFIG_SWIFT_INSTALL=y # Set to 'y' if you would like Packstack to install OpenStack # Metering (Ceilometer) CONFIG_CEILOMETER_INSTALL=n # Set to 'y' if you would like Packstack to install OpenStack # Orchestration (Heat) CONFIG_HEAT_INSTALL=n # Set to 'y' if you would like Packstack to install OpenStack # Clustering (Sahara) CONFIG_SAHARA_INSTALL=n # Set to 'y' if you would like Packstack to install OpenStack # Database (Trove) CONFIG_TROVE_INSTALL=n # Set to 'y' if you would like Packstack to install OpenStack Bare # Metal (Ironic) CONFIG_IRONIC_INSTALL=n # Set to 'y' if you would like Packstack to install the OpenStack # Client packages. An admin "rc" file will also be installed CONFIG_CLIENT_INSTALL=y # Comma separated list of NTP servers. Leave plain if Packstack # should not install ntpd on instances. CONFIG_NTP_SERVERS= # Set to 'y' if you would like Packstack to install Nagios to monitor # OpenStack hosts CONFIG_NAGIOS_INSTALL=n # Comma separated list of servers to be excluded from installation in # case you are running Packstack the second time with the same answer # file and don't want Packstack to touch these servers. Leave plain if # you don't need to exclude any server. EXCLUDE_SERVERS= # Set to 'y' if you want to run OpenStack services in debug mode. # Otherwise set to 'n'. CONFIG_DEBUG_MODE=y # The IP address of the server on which to install OpenStack services # specific to controller role such as API servers, Horizon, etc. CONFIG_CONTROLLER_HOST=192.168.101.2 # The list of IP addresses of the server on which to install the Nova # compute service CONFIG_COMPUTE_HOSTS=192.168.101.2 # The list of IP addresses of the server on which to install the # network service such as Nova network or Neutron CONFIG_NETWORK_HOSTS=192.168.101.2 # Set to 'y' if you want to use VMware vCenter as hypervisor and # storage. Otherwise set to 'n'. CONFIG_VMWARE_BACKEND=n # Set to 'y' if you want to use unsupported parameters. This should # be used only if you know what you are doing.Issues caused by using # unsupported options won't be fixed before next major release. CONFIG_UNSUPPORTED=n # The IP address of the VMware vCenter server CONFIG_VCENTER_HOST= # The username to authenticate to VMware vCenter server CONFIG_VCENTER_USER= # The password to authenticate to VMware vCenter server CONFIG_VCENTER_PASSWORD= # The name of the vCenter cluster CONFIG_VCENTER_CLUSTER_NAME= # (Unsupported!) The IP address of the server on which to install # OpenStack services specific to storage servers such as Glance and # Cinder. CONFIG_STORAGE_HOST=192.168.101.2 # (Unsupported!) The IP address of the server on which to install # OpenStack services specific to Sahara CONFIG_SAHARA_HOST=192.168.101.2 # To subscribe each server to EPEL enter "y" CONFIG_USE_EPEL=n # A comma separated list of URLs to any additional yum repositories # to install CONFIG_REPO= # To subscribe each server with Red Hat subscription manager, include # this with CONFIG_RH_PW CONFIG_RH_USER= # To subscribe each server with RHN Satellite,fill Satellite's URL # here. Note that either satellite's username/password or activation # key has to be provided CONFIG_SATELLITE_URL= # To subscribe each server with Red Hat subscription manager, include # this with CONFIG_RH_USER CONFIG_RH_PW= # To enable RHEL optional repos use value "y" CONFIG_RH_OPTIONAL=y # Specify a HTTP proxy to use with Red Hat subscription manager CONFIG_RH_PROXY= # Specify port of Red Hat subscription manager HTTP proxy CONFIG_RH_PROXY_PORT= # Specify a username to use with Red Hat subscription manager HTTP # proxy CONFIG_RH_PROXY_USER= # Specify a password to use with Red Hat subscription manager HTTP # proxy CONFIG_RH_PROXY_PW= # Username to access RHN Satellite CONFIG_SATELLITE_USER= # Password to access RHN Satellite CONFIG_SATELLITE_PW= # Activation key for subscription to RHN Satellite CONFIG_SATELLITE_AKEY= # Specify a path or URL to a SSL CA certificate to use CONFIG_SATELLITE_CACERT= # If required specify the profile name that should be used as an # identifier for the system in RHN Satellite CONFIG_SATELLITE_PROFILE= # Comma separated list of flags passed to rhnreg_ks. Valid flags are: # novirtinfo, norhnsd, nopackages CONFIG_SATELLITE_FLAGS= # Specify a HTTP proxy to use with RHN Satellite CONFIG_SATELLITE_PROXY= # Specify a username to use with an authenticated HTTP proxy CONFIG_SATELLITE_PROXY_USER= # Specify a password to use with an authenticated HTTP proxy. CONFIG_SATELLITE_PROXY_PW= # Set the AMQP service backend. Allowed values are: qpid, rabbitmq CONFIG_AMQP_BACKEND=rabbitmq # The IP address of the server on which to install the AMQP service CONFIG_AMQP_HOST=192.168.101.2 # Enable SSL for the AMQP service CONFIG_AMQP_ENABLE_SSL=n # Enable Authentication for the AMQP service CONFIG_AMQP_ENABLE_AUTH=n # The password for the NSS certificate database of the AMQP service CONFIG_AMQP_NSS_CERTDB_PW=PW_PLACEHOLDER # The port in which the AMQP service listens to SSL connections CONFIG_AMQP_SSL_PORT=5671 # The filename of the certificate that the AMQP service is going to # use CONFIG_AMQP_SSL_CERT_FILE=/etc/pki/tls/certs/amqp_selfcert.pem # The filename of the private key that the AMQP service is going to # use CONFIG_AMQP_SSL_KEY_FILE=/etc/pki/tls/private/amqp_selfkey.pem # Auto Generates self signed SSL certificate and key CONFIG_AMQP_SSL_SELF_SIGNED=y # User for amqp authentication CONFIG_AMQP_AUTH_USER=amqp_user # Password for user authentication CONFIG_AMQP_AUTH_PASSWORD=PW_PLACEHOLDER # The IP address of the server on which to install MariaDB or IP # address of DB server to use if MariaDB installation was not selected CONFIG_MARIADB_HOST=192.168.101.2 # Username for the MariaDB admin user CONFIG_MARIADB_USER=root # Password for the MariaDB admin user CONFIG_MARIADB_PW=<password> # The password to use for the Keystone to access DB CONFIG_KEYSTONE_DB_PW=<password> # Region name CONFIG_KEYSTONE_REGION=RegionOne # The token to use for the Keystone service api CONFIG_KEYSTONE_ADMIN_TOKEN=1e62eca2d03f4cf7901bfa459e62a8dd # The password to use for the Keystone admin user CONFIG_KEYSTONE_ADMIN_PW=<password> # The password to use for the Keystone demo user CONFIG_KEYSTONE_DEMO_PW=<password> # Kestone token format. Use either UUID or PKI CONFIG_KEYSTONE_TOKEN_FORMAT=UUID # Name of service to use to run keystone (keystone or httpd) CONFIG_KEYSTONE_SERVICE_NAME=keystone # The password to use for the Glance to access DB CONFIG_GLANCE_DB_PW=<password> # The password to use for the Glance to authenticate with Keystone CONFIG_GLANCE_KS_PW=<password> # Glance storage backend controls how Glance stores disk images. # Supported values: file, swift. Note that Swift installation have to # be enabled to have swift backend working. Otherwise Packstack will # fallback to 'file'. CONFIG_GLANCE_BACKEND=file # The password to use for the Cinder to access DB CONFIG_CINDER_DB_PW=<password> # The password to use for the Cinder to authenticate with Keystone CONFIG_CINDER_KS_PW=<password> # The Cinder backend to use, valid options are: lvm, gluster, nfs, # netapp CONFIG_CINDER_BACKEND=lvm # Create Cinder's volumes group. This should only be done for testing # on a proof-of-concept installation of Cinder. This will create a # file-backed volume group and is not suitable for production usage. CONFIG_CINDER_VOLUMES_CREATE=y # Cinder's volumes group size. Note that actual volume size will be # extended with 3% more space for VG metadata. CONFIG_CINDER_VOLUMES_SIZE=20G # A single or comma separated list of gluster volume shares to mount, # eg: ip-address:/vol-name, domain:/vol-name CONFIG_CINDER_GLUSTER_MOUNTS= # A single or comma seprated list of NFS exports to mount, eg: ip- # address:/export-name CONFIG_CINDER_NFS_MOUNTS= # (required) Administrative user account name used to access the # storage system or proxy server. CONFIG_CINDER_NETAPP_LOGIN= # (required) Password for the administrative user account specified # in the netapp_login parameter. CONFIG_CINDER_NETAPP_PASSWORD= # (required) The hostname (or IP address) for the storage system or # proxy server. CONFIG_CINDER_NETAPP_HOSTNAME= # (optional) The TCP port to use for communication with ONTAPI on the # storage system. Traditionally, port 80 is used for HTTP and port 443 # is used for HTTPS; however, this value should be changed if an # alternate port has been configured on the storage system or proxy # server. Defaults to 80. CONFIG_CINDER_NETAPP_SERVER_PORT=80 # (optional) The storage family type used on the storage system; # valid values are ontap_7mode for using Data ONTAP operating in # 7-Mode or ontap_cluster for using clustered Data ONTAP, or eseries # for NetApp E-Series. Defaults to ontap_cluster. CONFIG_CINDER_NETAPP_STORAGE_FAMILY=ontap_cluster # (optional) The transport protocol used when communicating with # ONTAPI on the storage system or proxy server. Valid values are http # or https. Defaults to http. CONFIG_CINDER_NETAPP_TRANSPORT_TYPE=http # (optional) The storage protocol to be used on the data path with # the storage system; valid values are iscsi or nfs. Defaults to nfs. CONFIG_CINDER_NETAPP_STORAGE_PROTOCOL=nfs # (optional) The quantity to be multiplied by the requested volume # size to ensure enough space is available on the virtual storage # server (Vserver) to fulfill the volume creation request. Defaults # to 1.0. CONFIG_CINDER_NETAPP_SIZE_MULTIPLIER=1.0 # (optional) This parameter specifies the threshold for last access # time for images in the NFS image cache. When a cache cleaning cycle # begins, images in the cache that have not been accessed in the last # M minutes, where M is the value of this parameter, will be deleted # from the cache to create free space on the NFS share. Defaults to # 720. CONFIG_CINDER_NETAPP_EXPIRY_THRES_MINUTES=720 # (optional) If the percentage of available space for an NFS share # has dropped below the value specified by this parameter, the NFS # image cache will be cleaned. Defaults to 20 CONFIG_CINDER_NETAPP_THRES_AVL_SIZE_PERC_START=20 # (optional) When the percentage of available space on an NFS share # has reached the percentage specified by this parameter, the driver # will stop clearing files from the NFS image cache that have not been # accessed in the last M minutes, where M is the value of the # expiry_thres_minutes parameter. Defaults to 60. CONFIG_CINDER_NETAPP_THRES_AVL_SIZE_PERC_STOP=60 # (optional) File with the list of available NFS shares. Defaults # to ''. CONFIG_CINDER_NETAPP_NFS_SHARES_CONFIG= # (optional) This parameter is only utilized when the storage # protocol is configured to use iSCSI. This parameter is used to # restrict provisioning to the specified controller volumes. Specify # the value of this parameter to be a comma separated list of NetApp # controller volume names to be used for provisioning. Defaults to # ''. CONFIG_CINDER_NETAPP_VOLUME_LIST= # (optional) The vFiler unit on which provisioning of block storage # volumes will be done. This parameter is only used by the driver when # connecting to an instance with a storage family of Data ONTAP # operating in 7-Mode and the storage protocol selected is iSCSI. Only # use this parameter when utilizing the MultiStore feature on the # NetApp storage system. Defaults to ''. CONFIG_CINDER_NETAPP_VFILER= # (optional) This parameter specifies the virtual storage server # (Vserver) name on the storage cluster on which provisioning of block # storage volumes should occur. If using the NFS storage protocol, # this parameter is mandatory for storage service catalog support # (utilized by Cinder volume type extra_specs support). If this # parameter is specified, the exports belonging to the Vserver will # only be used for provisioning in the future. Block storage volumes # on exports not belonging to the Vserver specified by this parameter # will continue to function normally. Defaults to ''. CONFIG_CINDER_NETAPP_VSERVER= # (optional) This option is only utilized when the storage family is # configured to eseries. This option is used to restrict provisioning # to the specified controllers. Specify the value of this option to be # a comma separated list of controller hostnames or IP addresses to be # used for provisioning. Defaults to ''. CONFIG_CINDER_NETAPP_CONTROLLER_IPS= # (optional) Password for the NetApp E-Series storage array. Defaults # to ''. CONFIG_CINDER_NETAPP_SA_PASSWORD= # (optional) This option is used to specify the path to the E-Series # proxy application on a proxy server. The value is combined with the # value of the netapp_transport_type, netapp_server_hostname, and # netapp_server_port options to create the URL used by the driver to # connect to the proxy application. Defaults to '/devmgr/v2'. CONFIG_CINDER_NETAPP_WEBSERVICE_PATH=/devmgr/v2 # (optional) This option is used to restrict provisioning to the # specified storage pools. Only dynamic disk pools are currently # supported. Specify the value of this option to be a comma separated # list of disk pool names to be used for provisioning. Defaults to # ''. CONFIG_CINDER_NETAPP_STORAGE_POOLS= CONFIG_IRONIC_DB_PW=PW_PLACEHOLDER # The password to use for Ironic to authenticate with Keystone CONFIG_IRONIC_KS_PW=PW_PLACEHOLDER # The password to use for the Nova to access DB CONFIG_NOVA_DB_PW=<password> # The password to use for the Nova to authenticate with Keystone CONFIG_NOVA_KS_PW=<password> # The overcommitment ratio for virtual to physical CPUs. Set to 1.0 # to disable CPU overcommitment CONFIG_NOVA_SCHED_CPU_ALLOC_RATIO=16.0 # The overcommitment ratio for virtual to physical RAM. Set to 1.0 to # disable RAM overcommitment CONFIG_NOVA_SCHED_RAM_ALLOC_RATIO=1.5 # Protocol used for instance migration. Allowed values are tcp and # ssh. Note that by defaul nova user is created with /sbin/nologin # shell so that ssh protocol won't be working. To make ssh protocol # work you have to fix nova user on compute hosts manually. CONFIG_NOVA_COMPUTE_MIGRATE_PROTOCOL=tcp # The manager that will run nova compute. CONFIG_NOVA_COMPUTE_MANAGER=nova.compute.manager.ComputeManager # Private interface for Flat DHCP on the Nova compute servers CONFIG_NOVA_COMPUTE_PRIVIF=eth1 # Nova network manager CONFIG_NOVA_NETWORK_MANAGER=nova.network.manager.FlatDHCPManager # Public interface on the Nova network server CONFIG_NOVA_NETWORK_PUBIF=eth0 # Private interface for network manager on the Nova network server CONFIG_NOVA_NETWORK_PRIVIF=eth1 # IP Range for network manager CONFIG_NOVA_NETWORK_FIXEDRANGE=192.168.32.0/22 # IP Range for Floating IP's CONFIG_NOVA_NETWORK_FLOATRANGE=10.3.4.0/22 # Automatically assign a floating IP to new instances CONFIG_NOVA_NETWORK_AUTOASSIGNFLOATINGIP=n # First VLAN for private networks CONFIG_NOVA_NETWORK_VLAN_START=100 # Number of networks to support CONFIG_NOVA_NETWORK_NUMBER=1 # Number of addresses in each private subnet CONFIG_NOVA_NETWORK_SIZE=255 # The password to use for Neutron to authenticate with Keystone CONFIG_NEUTRON_KS_PW=<password> # The password to use for Neutron to access DB CONFIG_NEUTRON_DB_PW=<password> # The name of the ovs bridge (or empty for linuxbridge) that the # Neutron L3 agent will use for external traffic, or 'provider' using # provider networks. CONFIG_NEUTRON_L3_EXT_BRIDGE=br-ex # Neutron metadata agent password CONFIG_NEUTRON_METADATA_PW=<password> # Set to 'y' if you would like Packstack to install Neutron LBaaS CONFIG_LBAAS_INSTALL=n # Set to 'y' if you would like Packstack to install Neutron L3 # Metering agent CONFIG_NEUTRON_METERING_AGENT_INSTALL=n # Whether to configure neutron Firewall as a Service CONFIG_NEUTRON_FWAAS=n # A comma separated list of network type driver entrypoints to be # loaded from the neutron.ml2.type_drivers namespace. CONFIG_NEUTRON_ML2_TYPE_DRIVERS=vxlan,flat # A comma separated ordered list of network_types to allocate as # tenant networks. The value 'local' is only useful for single-box # testing but provides no connectivity between hosts. CONFIG_NEUTRON_ML2_TENANT_NETWORK_TYPES=vxlan # A comma separated ordered list of networking mechanism driver # entrypoints to be loaded from the neutron.ml2.mechanism_drivers # namespace. CONFIG_NEUTRON_ML2_MECHANISM_DRIVERS=openvswitch # A comma separated list of physical_network names with which flat # networks can be created. Use * to allow flat networks with arbitrary # physical_network names. CONFIG_NEUTRON_ML2_FLAT_NETWORKS=* # A comma separated list of <physical_network>:<vlan_min>:<vlan_max> # or <physical_network> specifying physical_network names usable for # VLAN provider and tenant networks, as well as ranges of VLAN tags on # each available for allocation to tenant networks. CONFIG_NEUTRON_ML2_VLAN_RANGES= # A comma separated list of <tun_min>:<tun_max> tuples enumerating # ranges of GRE tunnel IDs that are available for tenant network # allocation. Should be an array with tun_max +1 - tun_min > 1000000 CONFIG_NEUTRON_ML2_TUNNEL_ID_RANGES= # Multicast group for VXLAN. If unset, disables VXLAN enable sending # allocate broadcast traffic to this multicast group. When left # unconfigured, will disable multicast VXLAN mode. Should be an # Multicast IP (v4 or v6) address. CONFIG_NEUTRON_ML2_VXLAN_GROUP= # A comma separated list of <vni_min>:<vni_max> tuples enumerating # ranges of VXLAN VNI IDs that are available for tenant network # allocation. Min value is 0 and Max value is 16777215. CONFIG_NEUTRON_ML2_VNI_RANGES=10:100 # The name of the L2 agent to be used with Neutron CONFIG_NEUTRON_L2_AGENT=openvswitch # A comma separated list of interface mappings for the Neutron # linuxbridge plugin (eg. physnet1:eth1,physnet2:eth2,physnet3:eth3) CONFIG_NEUTRON_LB_INTERFACE_MAPPINGS= # A comma separated list of bridge mappings for the Neutron # openvswitch plugin (eg. physnet1:br-eth1,physnet2:br-eth2,physnet3 # :br-eth3) CONFIG_NEUTRON_OVS_BRIDGE_MAPPINGS=external:br-ex # A comma separated list of colon-separated OVS bridge:interface # pairs. The interface will be added to the associated bridge. CONFIG_NEUTRON_OVS_BRIDGE_IFACES=br-ex:eth1 # The interface for the OVS tunnel. Packstack will override the IP # address used for tunnels on this hypervisor to the IP found on the # specified interface. (eg. eth1) CONFIG_NEUTRON_OVS_TUNNEL_IF= # VXLAN UDP port CONFIG_NEUTRON_OVS_VXLAN_UDP_PORT=4789 # To set up Horizon communication over https set this to 'y' CONFIG_HORIZON_SSL=n # PEM encoded certificate to be used for ssl on the https server, # leave blank if one should be generated, this certificate should not # require a passphrase CONFIG_SSL_CERT= # SSL keyfile corresponding to the certificate if one was entered CONFIG_SSL_KEY= # PEM encoded CA certificates from which the certificate chain of the # server certificate can be assembled. CONFIG_SSL_CACHAIN= # The password to use for the Swift to authenticate with Keystone CONFIG_SWIFT_KS_PW=<password> # A comma separated list of devices which to use as Swift Storage # device. Each entry should take the format /path/to/dev, for example # /dev/vdb will install /dev/vdb as Swift storage device (packstack # does not create the filesystem, you must do this first). If value is # omitted Packstack will create a loopback device for test setup CONFIG_SWIFT_STORAGES= # Number of swift storage zones, this number MUST be no bigger than # the number of storage devices configured CONFIG_SWIFT_STORAGE_ZONES=1 # Number of swift storage replicas, this number MUST be no bigger # than the number of storage zones configured CONFIG_SWIFT_STORAGE_REPLICAS=1 # FileSystem type for storage nodes CONFIG_SWIFT_STORAGE_FSTYPE=ext4 # Shared secret for Swift CONFIG_SWIFT_HASH=d93b741532ef49b8 # Size of the swift loopback file storage device CONFIG_SWIFT_STORAGE_SIZE=2G # The password used by Heat user to authenticate against MySQL CONFIG_HEAT_DB_PW=PW_PLACEHOLDER # The encryption key to use for authentication info in database CONFIG_HEAT_AUTH_ENC_KEY=1cf04f020eda47e2 # The password to use for the Heat to authenticate with Keystone CONFIG_HEAT_KS_PW=PW_PLACEHOLDER # Set to 'y' if you would like Packstack to install Heat CloudWatch # API CONFIG_HEAT_CLOUDWATCH_INSTALL=n # Set to 'y' if you would like Packstack to install Heat # CloudFormation API CONFIG_HEAT_CFN_INSTALL=n # Name of Keystone domain for Heat CONFIG_HEAT_DOMAIN=heat # Name of Keystone domain admin user for Heat CONFIG_HEAT_DOMAIN_ADMIN=heat_admin # Password for Keystone domain admin user for Heat CONFIG_HEAT_DOMAIN_PASSWORD=PW_PLACEHOLDER # Whether to provision for demo usage and testing. Note that # provisioning is only supported for all-in-one installations. CONFIG_PROVISION_DEMO=n # Whether to configure tempest for testing CONFIG_PROVISION_TEMPEST=n # The name of the Tempest Provisioning user. If you don't provide a # user name, Tempest will be configured in a standalone mode CONFIG_PROVISION_TEMPEST_USER= # The password to use for the Tempest Provisioning user CONFIG_PROVISION_TEMPEST_USER_PW=<password> # The CIDR network address for the floating IP subnet CONFIG_PROVISION_DEMO_FLOATRANGE=192.168.101.0/28 # A URL or local file location for the Cirros demo image used for # Glance CONFIG_PROVISION_CIRROS_URL=http://download.cirros-cloud.net/0.3.3/cirros-0.3.3-x86_64-disk.img # The uri of the tempest git repository to use CONFIG_PROVISION_TEMPEST_REPO_URI=https://github.com/openstack/tempest.git # The revision of the tempest git repository to use CONFIG_PROVISION_TEMPEST_REPO_REVISION=master # Whether to configure the ovs external bridge in an all-in-one # deployment CONFIG_PROVISION_ALL_IN_ONE_OVS_BRIDGE=n # Secret key for signing metering messages CONFIG_CEILOMETER_SECRET=573f8e6fbae34f6d # The password to use for Ceilometer to authenticate with Keystone CONFIG_CEILOMETER_KS_PW=<password> # Backend driver for group membership coordination CONFIG_CEILOMETER_COORDINATION_BACKEND=redis # The IP address of the server on which to install MongoDB CONFIG_MONGODB_HOST=192.168.101.2 # The IP address of the server on which to install redis CONFIG_REDIS_HOST=192.168.101.2 # The port on which the redis server listens CONFIG_REDIS_PORT=6379 # The password to use for the Sahara DB access CONFIG_SAHARA_DB_PW=PW_PLACEHOLDER # The password to use for Sahara to authenticate with Keystone CONFIG_SAHARA_KS_PW=PW_PLACEHOLDER # The password to use for the Trove DB access CONFIG_TROVE_DB_PW=PW_PLACEHOLDER # The password to use for Trove to authenticate with Keystone CONFIG_TROVE_KS_PW=PW_PLACEHOLDER # The user to use when Trove connects to Nova CONFIG_TROVE_NOVA_USER=admin # The tenant to use when Trove connects to Nova CONFIG_TROVE_NOVA_TENANT=services # The password to use when Trove connects to Nova CONFIG_TROVE_NOVA_PW=PW_PLACEHOLDER # The password of the nagiosadmin user on the Nagios server CONFIG_NAGIOS_PW=<password>
たぶん変えたのは、パスワード(PASSWORD/PW)とアドレス、CONFIG_PROVISION_DEMO=nとしたのとCONFIG_CEILOMETER_INSTALL=nにしたくらいかな。
7. packstackの実行
$ packstack --answer-file=packstack_answer.txt
8. OpenStackへログイン
無事インストールできたか確認するために、ブラウザで設定したアドレスにアクセスしてみる。
9. demoテナント/ユーザの作成
demo用のテナントを作成する。packstackを実行したディレクトリに"keystonerc_admin"というファイルがあるので、まずそれをsourceコマンドで読み込んでから、作業を継続。
$ source keystonerc_admin $ keystone tenant-list +----------------------------------+----------+---------+ | id | name | enabled | +----------------------------------+----------+---------+ | d567f9b8713546b9861f2c963892b13a | admin | True | | 43fc22fbdf0648d7ae06a09096883d6e | services | True | +----------------------------------+----------+---------+ $ keystone tenant-create --name demo +-------------+----------------------------------+ | Property | Value | +-------------+----------------------------------+ | description | | | enabled | True | | id | bd62eb96f2784abaacfd1d6affe90317 | | name | demo | +-------------+----------------------------------+ $ keystone user-create --name demo --tenant bd62eb96f2784abaacfd1d6affe90317 --pass <password> +----------+----------------------------------+ | Property | Value | +----------+----------------------------------+ | email | | | enabled | True | | id | 9e38aa7e4520483284487d802e818d80 | | name | demo | | tenantId | bd62eb96f2784abaacfd1d6affe90317 | | username | demo | +----------+----------------------------------+
10. ネットワークの作成
OpenStack上のテナントがネットワークに接続するためには、Neutronを利用して論理的なネットワークを作成してあげる必要があるので作る。ここでは、OpenStackインストールガイド RED HAT ENTERPRISE LINUX 7、CENTOS 7、FEDORA 20 版 - KILOの6章.networkingコンポーネントの追加の中の初期ネットワークの作成を参考にする。
最初は"net-list"コマンドが空で帰ってきてネットワークが無い状態。
$ source keystonerc_admin
$ neutron net-list
10.1 外部ネットワークの作成
まずは、外部ネットワーク]*1を作成。
$ neutron net-create ext-net --router:external True --provider:physical_network external --provider:network_type flat +---------------------------+--------------------------------------+ | Field | Value | +---------------------------+--------------------------------------+ | admin_state_up | True | | id | 06805329-9cab-4f62-af3e-8fc86c5473fb | | name | ext-net | | provider:network_type | flat | | provider:physical_network | external | | provider:segmentation_id | | | router:external | True | | shared | False | | status | ACTIVE | | subnets | | | tenant_id | d567f9b8713546b9861f2c963892b13a | +---------------------------+--------------------------------------+
10.2 外部ネットワークにサブネットを追加
次は、外部ネットワークにサブネットを追加。書式は下記。
$ neutron subnet-create ext-net --name ext-subnet --allocation-pool start=FLOATING_IP_START,end=FLOATING_IP_END --disable-dhcp --gateway EXTERNAL_NETWORK_GATEWAY EXTERNAL_NETWORK_CIDR
$ neutron subnet-create ext-net --name ext-subnet --allocation-pool start=192.168.101.32,end=192.168.101.63 --disable-dhcp --gateway 192.168.101.1 192.168.101.0/24 Created a new subnet: +-------------------+------------------------------------------------------+ | Field | Value | +-------------------+------------------------------------------------------+ | allocation_pools | {"start": "192.168.101.32", "end": "192.168.101.63"} | | cidr | 192.168.101.0/24 | | dns_nameservers | | | enable_dhcp | False | | gateway_ip | 192.168.101.1 | | host_routes | | | id | 33dd5210-5090-4af7-8510-0c61726620bf | | ip_version | 4 | | ipv6_address_mode | | | ipv6_ra_mode | | | name | ext-subnet | | network_id | 06805329-9cab-4f62-af3e-8fc86c5473fb | | tenant_id | d567f9b8713546b9861f2c963892b13a | +-------------------+------------------------------------------------------+
10.3 テナントネットワークの作成
次にテナントが利用するテナントネットワークを作成。
一回ブラウザでdemoユーザでログインして、Project -> Compute -> Access & Security -> API Access -> Download OpenStack RC Fileをクリック、rcファイルをダウンロードする。
$ source demo-openrc.sh
$
$ neutron net-create demo-net
Created a new network:
+-----------------+--------------------------------------+
| Field | Value |
+-----------------+--------------------------------------+
| admin_state_up | True |
| id | 98ed4034-a1d7-4aaf-813d-34905a254492 |
| name | demo-net |
| router:external | False |
| shared | False |
| status | ACTIVE |
| subnets | |
| tenant_id | bd62eb96f2784abaacfd1d6affe90317 |
+-----------------+--------------------------------------+
10.4 テナントネットワークのサブネットを作成
テナントネットワークのアドレスの範囲*2を192.168.50.0/24として、サブネットを作成。
$ neutron subnet-create demo-net --name demo-subnet --gateway 192.168.50.1 192.168.50.0/24 Created a new subnet: +-------------------+----------------------------------------------------+ | Field | Value | +-------------------+----------------------------------------------------+ | allocation_pools | {"start": "192.168.50.2", "end": "192.168.50.254"} | | cidr | 192.168.50.0/24 | | dns_nameservers | | | enable_dhcp | True | | gateway_ip | 192.168.50.1 | | host_routes | | | id | d4f16b69-ddb2-4779-a608-b871fe824acd | | ip_version | 4 | | ipv6_address_mode | | | ipv6_ra_mode | | | name | demo-subnet | | network_id | 98ed4034-a1d7-4aaf-813d-34905a254492 | | tenant_id | bd62eb96f2784abaacfd1d6affe90317 | +-------------------+------------------------------------------------
10.5 ルータの作成
外部ネットワークとテナントネットワークを接続するルータを作成する。
$ neutron router-create demo-router Created a new router: +-----------------------+--------------------------------------+ | Field | Value | +-----------------------+--------------------------------------+ | admin_state_up | True | | external_gateway_info | | | id | 7ca669ec-6bec-4da2-8887-163825bdb492 | | name | demo-router | | routes | | | status | ACTIVE | | tenant_id | bd62eb96f2784abaacfd1d6affe90317 | +-----------------------+--------------------------------------+
10.6 ルータをdemoサブネットへ接続
$ neutron router-interface-add demo-router demo-subnet Added interface e9bb01dd-0b39-4a36-a39d-3c8fb2a2f222 to router demo-router.
10.7 外部ネットワークをGWに指定してルータに接続
$ neutron router-gateway-set demo-router ext-net Set gateway for router demo-router
11. インスタンスの起動とfloating ipの割り付け
あとは、セキュリティグループの設定で、外部からのsshやpingを受け付けるように設定したあと、インスタンスを起動してfloating ipを割り付ければ、該当インスタンスに外からアクセスできるはず。